Battlefield 2042’s Map Design Under Scrutiny: Are Smaller Maps Hurting the Player Experience?
Popular Now
 Rust
Rust
 Valorant
Valorant
 EA SPORT FC 25
EA SPORT FC 25
 Among Us
Among Us
 Schedule I
Schedule I
 Fall Guys
Fall Guys
 Toca Boca World
Toca Boca World
 God of War Ragnarök
God of War Ragnarök
 League of Legends
League of Legends
 BeamNG.drive
BeamNG.drive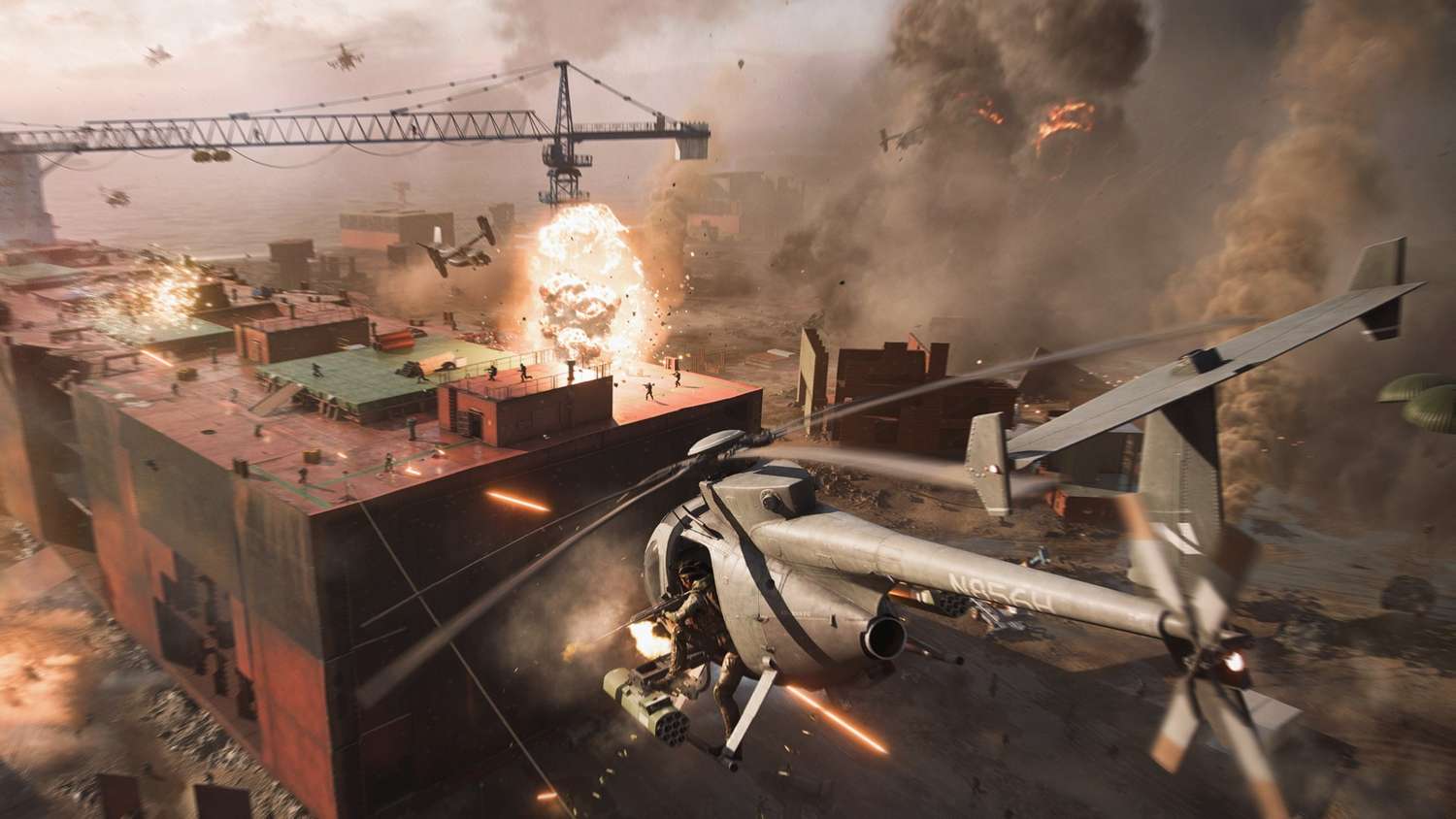 
The revered Battlefield franchise has long been synonymous with expansive battlegrounds, colossal player counts, and the exhilarating chaos of large-scale warfare. From the sprawling deserts of El Alamein to the urban labyrinths of Grand Bazaar, map design has consistently been a cornerstone of the series’ identity, dictating pacing, strategic depth, and overall player enjoyment. However, with the release of Battlefield 2042, widely considered by many as the spiritual successor to ‘Battlefield 6’, a growing chorus of criticism has emerged regarding its map philosophy. Many players and critics alike contend that several of Battlefield 2042’s maps feel surprisingly constrained, even small, for the game’s advertised 128-player battles, raising significant questions about the long-term health of its player engagement metrics and position within the competitive gaming industry trends.
Historically, Battlefield maps were celebrated for their careful balance of open terrain, cover, vantage points, and distinct sectors that facilitated a dynamic push-and-pull between teams. Iconic maps like Wake Island, Caspian Border, and Golmud Railway offered a sense of grand scale, allowing diverse playstyles – from audacious vehicle assaults to stealthy infantry flanking maneuvers. This design philosophy created memorable moments and fostered strategic thinking, making each conquest feel earned. The expectation for Battlefield 2042’s maps, particularly given its leap to 128 players on PC and next-gen consoles, was a further evolution of this grand vision. What materialized, however, has often been perceived as a departure, leading to frustration among the dedicated fanbase and impacting the game’s critical reception.
The Core Issue: Perceived Smallness Amidst Vastness
While some of Battlefield 2042’s environments are geographically vast, the criticism isn’t necessarily about the total square footage. Instead, it targets the *playable* area, the density of cover, and the logical flow of combat within these spaces. Maps such as Kaleidoscope, Manifest, and the original version of Hourglass quickly became emblematic of this problem. Kaleidoscope, with its central skyscraper and surrounding urban sprawl, often devolved into a congested meatgrinder in key objective zones, while large sections of the map felt empty or irrelevant. Manifest, set in a shipping yard, presented a visually cluttered but strategically shallow experience, where the lack of varied terrain made flanks predictable and engagements repetitive.
- Lack of Varied Cover: Many maps feature vast, open spaces without adequate cover, leaving infantry vulnerable to vehicle fire and long-range engagements. This reduces tactical options and encourages static play.
- Poor Objective Placement: Objectives are sometimes placed in isolated or difficult-to-defend locations, leading to unbalanced conquest flows and frustrating spawn traps.
- Unused Map Sections: Despite their overall size, significant portions of certain maps are often ignored by the flow of battle, making the actual combat zone feel much smaller and more linear than intended for 128 players.
- Vehicle Dominance: The combination of open spaces and limited infantry cover often empowers vehicles excessively, leading to a less balanced rock-paper-scissors dynamic that is a hallmark of Battlefield gameplay.
 Impact on Gameplay Experience and Player Retention
Impact on Gameplay Experience and Player Retention
The perceived smallness and poor design of key maps have had a palpable impact on the core Battlefield experience. The sense of epic, strategic warfare often gives way to chaotic, often frustrating skirmishes. This directly affects player retention, a critical factor in the success of any live service game in today’s competitive digital entertainment market. When maps feel repetitive or unbalanced, players are more likely to disengage, impacting everything from active user counts to potential monetization strategies through battle passes and cosmetic sales.
The lack of engaging map design can stifle the very essence of Battlefield: teamwork and large-scale strategy. When flanking routes are limited, and objective pushes are funnelled into predictable chokepoints, the nuanced interplay between infantry, vehicles, and air support diminishes. This can lead to a less rewarding experience for veteran players seeking depth and variety, and a more alienating one for newcomers struggling to understand the flow of battle. The absence of diverse, well-thought-out environments undermines the game’s potential to become a leading title in the AAA game development space and affects its standing in the broader gaming community.
Developer Challenges and Iterative Improvements
Developing maps for a 128-player environment presents considerable technical and design challenges. Ensuring performance, visual fidelity, and engaging gameplay across such a vast scale requires immense resources and intricate planning. DICE, the developer behind Battlefield, has acknowledged many of these criticisms and has actively embarked on significant map reworks and improvements post-launch. For instance, maps like Kaleidoscope, Breakaway, and Manifest have received substantial updates, adding more cover, adjusting objective layouts, and improving terrain elevation to create more dynamic combat zones. These iterative changes are crucial for the game’s long-term viability and demonstrate a commitment to addressing player feedback.
However, these reworks, while positive, highlight the initial missteps in design. The expectation from players is often a polished experience at launch, especially for a flagship title from a publisher like Electronic Arts. The necessity of extensive post-launch re-evaluations affects not only immediate sales but also shapes public perception and critical reviews, which are vital for future entries in the series. The financial implications for publishers in the highly competitive gaming industry are substantial, as initial impressions heavily influence user acquisition costs and lifetime customer value. Investing in robust game analytics and comprehensive playtesting during development stages is paramount to avoid such challenges.
The Economic Underpinnings of Map Design
Beyond immediate player satisfaction, map design has significant economic ramifications for a title like Battlefield 2042. A game that struggles with fundamental gameplay elements, such as map flow, often sees reduced digital game sales, lower engagement with premium content like Battle Passes, and a diminished opportunity for long-term revenue streams. The cost of developing and subsequently re-working maps is substantial, impacting profitability and resource allocation for future content. For publishers, maintaining a strong, active player base is crucial for sustaining a live service model, which relies on consistent player spending and retention. Positive word-of-mouth and strong reviews are invaluable assets, contributing to brand loyalty and driving future purchases, making excellent core design a true high-value investment.
The current landscape of the video game market demands that developers not only innovate but also meticulously refine their core mechanics. When a game like Battlefield, a titan of the first-person shooter genre, faces criticism over something as fundamental as its map design, it serves as a stark reminder of the intricate balance required in modern AAA game development. The interplay between ambitious scale, technical execution, and player-centric design dictates success, influencing everything from individual player experiences to multi-million dollar corporate strategies. A poorly received map set can directly lead to lost revenue and a tarnished reputation, impacting future game development budgets and overall strategic direction.
 Looking Ahead: A Lesson for Future Battlefield Titles
Looking Ahead: A Lesson for Future Battlefield Titles
The lessons learned from Battlefield 2042’s map design challenges are invaluable for the future of the franchise. It underscores the critical importance of balancing scale with tactical density, ensuring every square meter of a map contributes meaningfully to the gameplay experience. Future Battlefield titles must not only push graphical boundaries but also re-evaluate what truly makes a large-scale battle map engaging for diverse playstyles. Prioritizing robust cover, multiple flanking opportunities, and clear, intuitive objective layouts for all player counts will be essential. Continuous engagement with community feedback and thorough internal playtesting throughout the development cycle can mitigate these issues proactively.
In conclusion, while Battlefield 2042 aimed for unprecedented scale with its 128-player battles, the execution of its map design has been a significant point of contention. The perception of ‘smaller’ or less effective playable areas within vast environments has impacted the game’s core gameplay loop and challenged the high expectations set by the franchise’s legacy. As the gaming industry evolves, the emphasis on robust, player-centric map design remains paramount, serving as a critical differentiator in a crowded market and dictating the ultimate success and longevity of even the most anticipated titles.








 Impact on Gameplay Experience and Player Retention
Impact on Gameplay Experience and Player Retention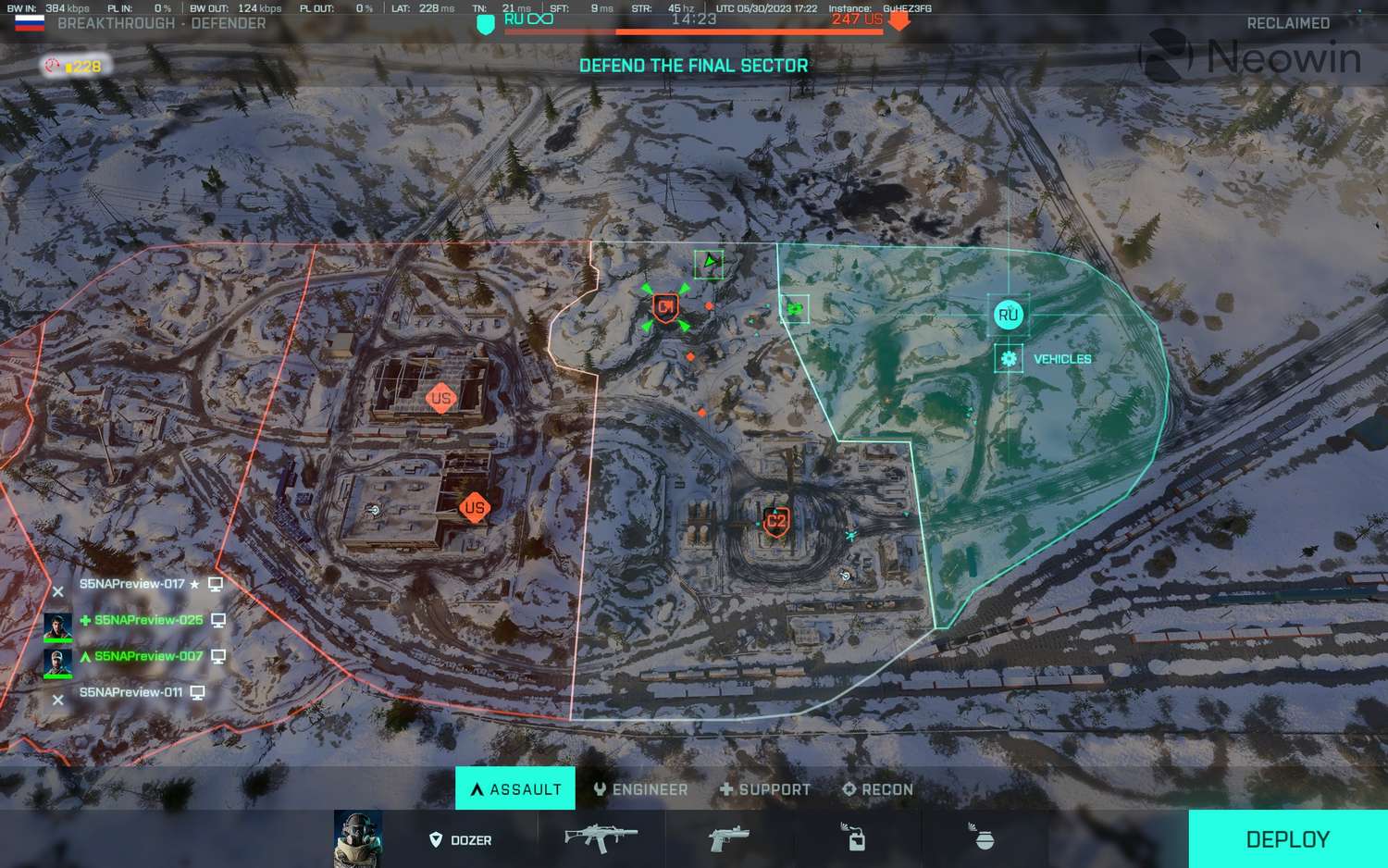 Looking Ahead: A Lesson for Future Battlefield Titles
Looking Ahead: A Lesson for Future Battlefield Titles